A disruptive technological concept has emerged, promising to reshape industries and redefine how we interact with the physical world. This concept is known as the Digital Twin.
A Digital Twin is a virtual replica of a physical object or system, created by integrating real-time data and advanced analytics. It is a digital mirror, reflecting the real-world entity’s properties, behaviors, and performance. By presenting the capability of generating simulations and analyses of complex systems the digital twin has enabled organizations to gain profound insights, optimize processes, and make more informed decisions.
This technology has been used in industrial contexts to raise productivity by planning and optimizing the process of data collection and analysis through a continuous flow of information between a real asset and a digital replica. However, Digital Twins can be categorized into various types, each tailored to specific applications and industries.
As technology continues to advance, the potential applications of digital twins are expanding. By harnessing the power of digital twins, organizations can unlock new opportunities, drive innovation, and achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and performance. Still, before exploring what companies can achieve with this technology, we need to understand what defines a Digital Twin.
What is a Digital Twin?
A Digital Twin is a dynamic, virtual representation of a physical object, process, or system that evolves alongside its real-world counterpart through continuous data exchange. This technology, which plays a pivotal role in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, embodies core principles of digitization, decentralization, modularity, and real-time operation.
The concept of Digital Twins was first introduced in 2002 by Michael Grieves as part of Product Lifecycle Management (PLM). Since then, it has evolved significantly, with applications spanning industries like manufacturing, healthcare, energy, urban planning, and beyond.
In this context, building a Digital Twin requires robust data acquisition, which can be achieved through various techniques. Sensors embedded in the physical asset are a common method, allowing to collect real-time data on performance, condition, and environmental factors. However, data acquisition extends beyond sensors. Techniques like Reality Capture through 3D scanning, photogrammetry, and high-resolution imaging are often used to create highly accurate virtual models. Additionally, information from existing documentation, such as blueprints, CAD models, and maintenance records, can be integrated into the Digital Twin to enrich its accuracy and functionality.
In this manner, this continuous influx of data is processed through advanced technologies such as cloud computing, spatial computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML). The resulting virtual model not only mirrors the physical counterpart but also enhances it by simulating scenarios, optimizing performance, and enabling predictive insights. As industries adopt Digital Twins, they are unlocking unprecedented levels of efficiency, innovation, and sustainability.
The Evolution of Digital Twins
Originally conceived as a tool for Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), Digital Twins have grown to become a transformative technology across numerous industries. One of the earliest notable applications was by NASA, which used Digital Twins to monitor and predict aircraft conditions during launches, enhancing safety and performance. Today, their potential extends far beyond aerospace. In healthcare, for example, researchers are exploring how Digital Twins could enable personalized medicine by tailoring treatments based on virtual replicas of individual patients, revolutionizing patient care. But how exactly does a Digital Twin differentiate from a mere digital scenario simulation?
Differentiating Digital Twins from Simulations
While Digital Twins and simulations may seem similar, they serve fundamentally different purposes. Simulations are designed to create hypothetical scenarios, offering insights based on predefined variables and models. In contrast, Digital Twins provide a real-time, dynamic connection between physical assets and their virtual counterparts. This is made possible by the continuous exchange of data, allowing Digital Twins to reflect and respond to real-world conditions as they evolve. This distinction makes Digital Twins valuable for monitoring, optimizing, and predicting performance in a way traditional simulations cannot achieve.
Digital Twin levels according to the ability to exchange data
Digital Twin can be used in many activities, the technology has a lot of different concepts surrounding it. From all these definitions, researchers from the Fraunhofer Austria Research GmbH differentiate them from the level of integration of the technology with the real world. All of them have in common the digital representation of an existing asset, and the distinction is the ability to exchange data. That being said, these are the 3 main models:
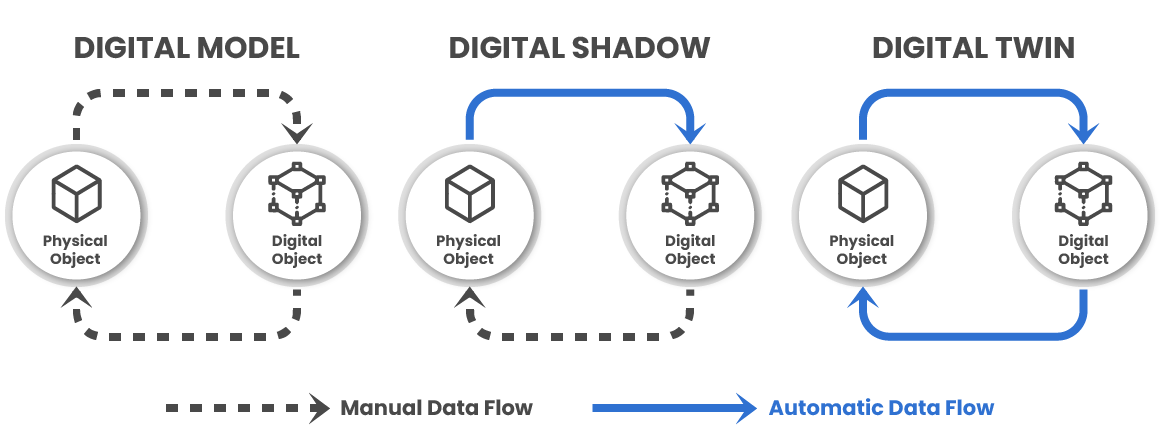
- Digital Model: The Digital Model doesn’t automate the data exchange from the physical to the digital model. All the data flow is done manually, furthermore, no change in the state of the physical or digital model has direct consequences for either of them;
- Digital Shadow: Different from the Digital Model, it has an automatic flow of data from the physical to the digital shadow. A change in the physical object can interfere with the digital, but the opposite does not occur;
- Digital Twin: There’s a flow of data between the physical asset and the digital and vice versa. As the Digital Shadow, the physical can control the digital, but also the digital interferes with the physical in this case. This constant flow fully integrated is what makes a Digital Twin.
Types of Digital Twin
Digital Twins can be categorized into four primary types, each tailored to specific applications and levels of complexity. These categories help organizations target the right use cases, from individual components to entire processes.
1. Component/Part Twins
This is the most granular type of Digital Twin, representing an individual component or part within a larger system. Examples include motors, sensors, or valves. This type is particularly useful for monitoring the health, performance, and operational efficiency of specific parts. By analyzing real-time and historical data, organizations can identify wear, malfunctions, or inefficiencies early, enabling predictive maintenance. This helps extend the component’s lifecycle and minimizes unexpected downtime.
2. Asset Twins
An Asset Twin is a digital replica of a physical asset comprising multiple interconnected components. Examples include machines, vehicles, or even buildings. Asset Twins provide a holistic view of the asset’s overall performance and condition. Organizations can optimize asset utilization, reduce operational costs, and improve uptime by aggregating data from individual and other sources. For instance, in manufacturing, Asset Twins can track a machine’s performance across its lifespan, helping to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
3. System/Unit Twins
A System Twin represents a collection of interconnected assets that work together to perform a specific function. Examples include production lines, HVAC systems, and renewable energy grids. This type of Digital Twin is crucial for analyzing and optimizing the behavior of complex systems. Organizations can simulate different operational scenarios, predict potential bottlenecks, and fine-tune system interactions for maximum efficiency. For example, in a power plant, a System Twin can help optimize energy generation, storage, and distribution by analyzing the interplay of various subsystems.
4. Process Twins
A Process Twin is the most comprehensive type, capturing the entire workflow or process from start to finish. Examples include manufacturing processes, supply chain operations, or service delivery pipelines. Process Twins integrate data from diverse sources such as IoT devices, enterprise systems, and operational records to create a complete picture of the process. Organizations can achieve greater productivity, quality control, and cost savings by identifying inefficiencies, predicting disruptions, and optimizing workflows. For example, in logistics, a Process Twin might track goods from production to delivery, ensuring timely fulfillment while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
What can be achieved with Digital Twin technology?
The term “Digital Twin” is often overused and misunderstood, with many solutions falling short of the true definition. However, when implemented effectively, Digital Twin technology can revolutionize industrial operations, offering measurable benefits that enhance efficiency, safety, and decision-making.
The rise and fall of Digital Twins
Despite the growing interest, several factors have limited the effective adoption of Digital Twins across industries. One major issue is its implementation complexity, which often demands advanced technical expertise that organizations may lack. Additionally, the effectiveness of a Digital Twin depends heavily on the quality of its underlying data, and many projects fail due to inaccurate or unreliable information. Thus, integration with existing legacy systems, which are often built on disparate and outdated technologies, presents another significant challenge, frequently causing delays and increased costs.
The lack of standardized frameworks and methodologies has also created inconsistencies, making it challenging for organizations to adopt Digital Twins at scale. Indeed, many existing solutions fail to address specific industrial challenges, offering limited practical value.
Furthermore, scalability has been a recurring issue, with Digital Twins often tailored for single-use cases, requiring significant time and resources to adapt to new problems. For this purpose, Vidya tackles these obstacles directly, providing scalable, data-driven solutions tailored to address the pressing challenges industries face today.
A Digital Twin made for Complex Industries
Vidya’s Digital Twin platform goes beyond simply mirroring assets. It leverages advanced spatial computing, artificial intelligence, and simulation technologies to deliver actionable insights and improve operational performance. Unlike many other solutions that provide static representations or isolated datasets, Vidya offers a comprehensive digital ecosystem that integrates historical and real-time data. This enables organizations to gain a deep understanding of their assets and processes while unlocking the full potential of their operational data.
Beyond that, Vidya’s technology also incorporates artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict maintenance needs, optimize workflows, and enhance safety protocols. This predictive capability helps managers anticipate potential issues, avoid costly unplanned downtime, and optimize resource allocation. By delivering a unified, scalable solution, Vidya ensures its Digital Twin technology can address a broad range of operational and maintenance challenges across industries.
Conclusion
Furthermore, Digital Twin technology represents a revolutionary leap in how industries interact with and manage their assets, systems, and processes. From its origins in Product Lifecycle Management to its transformative applications across manufacturing, healthcare, energy, and beyond, Digital Twins have proven their potential to drive efficiency, optimize performance, and enable predictive decision-making.
While challenges such as complexity, data quality, and scalability have hindered adoption in the past, advancements in AI, machine learning, and spatial computing are overcoming these barriers. By bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds, this technology is reshaping industries and setting the foundation for a smarter, more connected future.