2024 surely was a year to remember for technology, from AI being central to every industrial innovation, to advancements in renewable energy that accelerated the transition to a greener future. As we step into 2025, the question looms: which of these technologies—and others—will take the spotlight and shape the trajectory of our world?
1. Sci-fi robotics
Remember those movies that pictured robots as an integral part of society? Well, 2025 might be the year that brings this to reality. Despite being a highly anticipated technology, recent advancements are making these innovations available to a wider range of consumers.
Polyfunctional robots
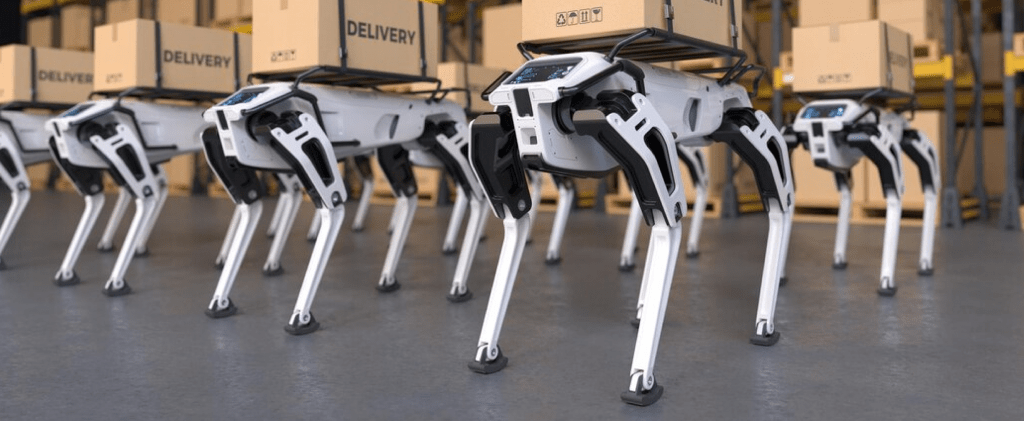
Polyfunctional robots perfectly illustrate this scenario. These machines are designed to perform multiple tasks or switch seamlessly between roles depending on operational demands. An example of a polyfunctional robot might be a platform capable of carrying payloads and assembling different equipment components depending on the assigned task. Another example is a quality control robot capable of inspecting whether a part was properly installed and ensuring no debris in or around the workspace.
A robot arm might handle electric vehicle components one day and shift to assembling components the next, all without requiring extensive reprogramming. According to Gartner, enterprises will likely deploy a handful of robots (or even a single robot), then scale up as they see benefit or in response to production demands.
Robotaxis
Robotaxis is paving the way for fully autonomous urban transportation, leveraging advanced image processing and sensor technologies to navigate city streets. Autonomous ride-hailing services are already operational in some American cities, but especially in China, where at least 19 cities are testing robotaxis and robo-buses with over 16,000 test licenses. According to S&P Global, China’s strong push for automated driving, bolstered by significant government support and regulatory frameworks, positions it as a potential leader in developing Autonomous Vehicles (AV) technology relative to the commercialization of the AV industry.
2. Spatial Computing
By merging the physical and digital environments through 3D interactions, Spatial Computing offers a spectrum of experiences from fully immersive virtual environments to augmented real-world scenarios. Seamless interaction between these domains opens avenues for enhanced visualization and deeper insights. According to Deloitte, the Spatial Computing market is projected to grow at a rate of 18.2% between 2025 and 2033.

Indeed, one of the defining features of Spatial Computing is its ability to understand and interpret spatial relationships in real-time. And, by comprehending the user’s surroundings, systems can accurately place and manipulate digital content within the physical space, creating a truly immersive experience. Deloitte also stated that real-time simulations have emerged as the technology’s primary use case, but the possibilities are endless. As Spatial Computing continues to evolve, its ability to seamlessly bridge physical and digital realms is set to redefine industries and enhance daily interactions.
3. Even more AI
Artificial intelligence will continue to dominate technological advancements in 2025. With its ability to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make intelligent decisions in real-time, AI is no longer confined to niche applications—it is becoming a catalyst of innovation and efficiency. For its next steps, the focus is shifting toward AI systems that are not only reactive but also proactive, leveraging context awareness and continuous learning to adapt to ever-changing environments.
Generative AI
Generative AI is still at this technology forefront, creating personalized experiences in various industries. Indeed, this technology has already revolutionized a wide range of areas by enabling machines to create text, images, and even complex designs. But its next steps promise even greater transformation, mainly focusing on improving contextual understanding and creative autonomy. Future interactions of GenAI will move beyond simple prompts to engage in richer, ongoing dialogues with users, adapting its responses to nuanced feedback.
According to MIT Technology Review, unlike previous models well suited for language tasks like writing and editing, ChatGPT’s next improvement focuses on multistep “reasoning”, the type of process required for advanced mathematics, or coding. It uses a “chain of thought” technique, according to OpenAI. “It learns to recognize and correct its mistakes. It learns to break down tricky steps into simpler ones. It learns to try a different approach when the current one isn’t working”, the company wrote in a blog post on its website.

Edge AI
Another AI application taking the spotlight in 2025 is Edge AI. This technology is emerging due to the rising demand for faster, more secure, and localized data processing. As industries grapple with real-time decision-making and data privacy challenges, Edge AI offers a solution that aligns perfectly with these needs. Certainly, the ability to process information directly on devices—be it a factory robot, a self-driving car, or a medical device—eliminates the delays of cloud-based systems and ensures greater control over sensitive data.
Edge AI involves processing data locally on devices rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This approach reduces latency and enhances data privacy, which is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles and IoT devices. The integration of edge AI is expected to expand, supporting more responsive and intelligent systems across various applications.
Small Language Models (SLMs)
Small Language Models (SLMs) are emerging as a practical alternative to their larger counterparts, offering focused capabilities with significantly lower computational and energy demands. One of the key advantages of SLMs is their ability to operate effectively on edge devices, making them ideal for environments where data privacy and low latency are critical. Indeed, SLMs offer the advantage of being trainable in local datasets, their simplified architectures enhance interpretability, and their compact size facilitates deployment on mobile devices.
Thus, the compact size of SLMs and reduced resource requirements make them ideal for deployment in environments where computational power and memory are limited. According to the Data Scientist Nagesh Mashette, deploying small language models involves a trade-off. Due to their training on smaller datasets, SLMs possess more constrained knowledge bases compared to their Large Language Model (LLM) counterparts.
4. Cyber security
In an increasingly interconnected industrial landscape, cybersecurity is no longer an option but a necessity. According to a report from ABI Research, one in four industrial enterprises had to halt operations due to a cyberattack temporarily. Thus, as companies adopt IoT devices, autonomous systems, and cloud web services, the attack surface for cyber threats expands significantly. In 2025, cybersecurity is expected to evolve into a more proactive and structured discipline.

One of the most critical trends shaping the future of cybersecurity in industrial operations is–of course–integrating AI. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, these tools can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying anomalies and potential breaches before they escalate into significant incidents. This capability is especially crucial for industrial enterprises, as it enables predictive threat detection and automated incident response.
5. 6G
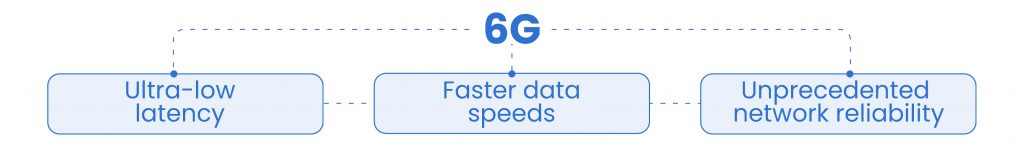
Complementary to the need for stronger security, this era’s interconnectedness will require a bigger digital infrastructure to support it. This is where 6G comes in. Although still in the development phase, this technology is projected to become a game-changer by offering ultra-low latency, faster data speeds, and unprecedented network reliability. According to the European Commission, 6G has the potential to bring together fields such as connectivity, robotics, cloud, and secure and trustworthy commerce. Despite estimates of consolidated implementation only in 2030, some companies (Apple, Huawei, etc.) and research institutes are already testing the sixth generation of wireless connectivity.
Conclusion
As we look ahead to 2025, the technologies shaping our journey promise to transform industries and our everyday lives in ways previously imagined only in science fiction. From the rise of polyfunctional robots and autonomous transportation to the immersive possibilities of Spatial Computing and the ever-evolving capabilities of AI, we are on the brink of a new technological era. Despite challenging us to adapt and harness their potential responsibly, these innovations will redefine how we tackle efficiency and functionality.