AI’s growth scenario
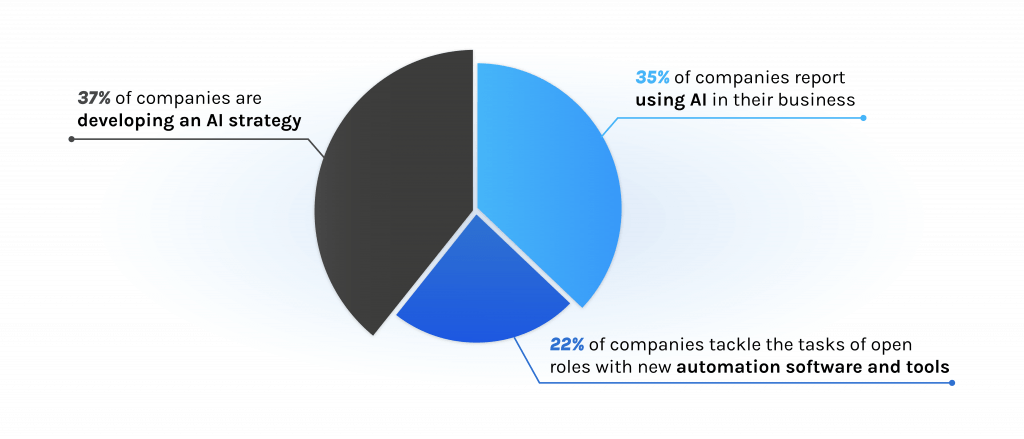
From its early days as a theoretical concept to today’s omnipresent reality, AI’s journey has been characterized by exponential growth. According to a 2022 IBM research, more than a third of companies (35%) report the use of AI in their business, a four-point increase from 2021. This illustrates a key change in the way we face reality, but different from other technological revolutions: today’s tool learns from its own experience at increasingly higher speed and scale.
These tools are programmed to have a human-like thought process. Moreover, they are now a reality in the routine of millions of people, not only addressing broad spectrum labor but increasing safety by freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and strategic responsibilities. Artificial Intelligence has become a catalyst for society’s innovation and sustainable growth.
AI’s boom has been driven by a combination of theoretical advancements, increased computational power, availability of data, and interdisciplinary collaboration. As AI continues to evolve, it holds the promise of transforming industries, solving complex problems, and reshaping the way we interact with technology and the world around us.
How are we benefiting from AI?
‘’This new technology can help people everywhere improve their lives.’’ – Bill Gates
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as one of the most transformative technological advancements of the 21st century, reshaping industries, economies, and the way we live our lives. But how exactly is it doing that?
- Enhanced technique
Similar to the past technological revolutions, the emergence of artificial intelligence as the driving force behind Industry 4.0 has changed the conditions under which workers handle their activities. AI technologies have the capacity to automate repetitive tasks, significantly increasing efficiency and productivity. For logistics, AI-powered robots and algorithms streamline production lines, optimize supply chains, and are not exposed to human error in supply chains. - Improved Decision-Making
AI systems have the ability to analyze vast amounts of data at speeds beyond human capability. This data-driven approach empowers businesses and organizations to make informed decisions based on accurate insights. AI can forecast future outcomes based on historical data and trends. However, human oversight is crucial to ensure that AI-driven decisions align with broader goals and values. - Detection and Monitoring
Within the realm of AI, the capabilities of machine vision have revolutionized security and detection processes. It serves as a highly accurate pattern recognition tool, enhancing areas such as medicine by identifying cancer cells or agriculture by detecting pests in the crop. The technology enables computers to see, analyze, and understand their surroundings in the same way the human visual perception does. - Personalized Time Management
AI-empowered personal assistants and productivity tools have transformed the way individuals manage their time. These tools can analyze user behavior, preferences, and schedules to provide customized suggestions for task prioritization, time allocation, and even breaks. By helping individuals optimize their daily routines, AI contributes to increased work efficiency and reduced stress. - Accessibility and Inclusion
AI-driven technologies have the potential to enhance accessibility and inclusion for individuals with disabilities. Voice recognition and natural language processing allow people with mobility challenges to interact with devices using their voices. AI has the potential to break down barriers and create a more inclusive society by providing innovative solutions that cater to the unique needs of individuals. - Forecasting
By analyzing historical patterns, market trends, and various external factors, AI-driven forecasting models can provide insights that traditional methods might overlook. The ability of AI to detect subtle correlations and predict potential outcomes based on complex interactions enables organizations to anticipate changes and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Which are the main areas affected by AI?
Artificial intelligence is helping to break down barriers that were previously impossible to overcome. In this sense, multiple areas have been affected by AI’s innovations, showcasing solutions that are reshaping how society deals with its most challenging problems. Here are some of the areas most impacted by the power of AI:
Medicine
AI’s implementation into medicine marks a paradigm shift in healthcare practices. It has demonstrated remarkable accuracy when it comes to tasks involving diagnosis. The integration of Machine Vision and Machine Learning, which will be further discussed in detail, has been crucial to aid clinicians in detecting subtle anomalies that may not be apparent to the human eye.
A 2018 study by Chiba University’s Center for Artificial Intelligence Research in Therapeutics (CAIRT) used machine learning techniques based on 32 blood markers in ovarian cancer patients before treatment. They found a group of early-stage cancer patients with poor prognosis. This finding helped researchers develop personalized treatments for this group of patients.
Agriculture
AI is revolutionizing agriculture by bringing data-driven solutions to farming practices. It enables the enhancement of crop monitoring processes, detection of diseases and pests, and optimization of harvests. The integration of AI-powered precision farming, predictive analytics, and optimized resource management is helping farmers produce more food, with better quality and fewer resources, contributing to global food security and sustainable agricultural practices.
Additionally, AI’s potential is not limited to its expectations, as the global market size of smart agriculture is expected to grow from approximately 15 billion U.S. dollars in 2022 to 33 billion U.S. dollars by 2027. In this sense, AI is driving rapid progress in digitalization across the agriculture value chain
Moving beyond its impact on those fundamental areas, AI’s transformative potential extends to various other sectors, with the energy industry standing as a prime example. Just as AI has brought data-driven solutions to farming, it’s also spearheading revolutionary changes in the energy sector. This energy industry, which has been a source of technological innovations for decades, is now leveraging AI to drive efficiency, cost reduction, environmental sustainability, and enhanced decision-making. Let’s delve into the forefront of AI’s journey within the industrial landscape:
The energy industry
Since the last century, most technological innovations have emerged from the industry, and with AI it’s no different. The frontline of AI’s advancements undoubtedly lies in the industry. These innovations are changing the way companies face their activities, bringing more efficiency, reducing costs, improving environmental sustainability, and enabling more effective decision-making. In this sense, here are the main frontiers of AI’s industrial journey:
Machine Vision
Machine vision represents the ability of a computer to see. It functions through high-definition cameras that capture images from the surrounding environment. These images are then trained as information through visual refinement algorithms, where filters are used to enable the recognition of behavioral patterns in the images.
It uses a convolutional neural network (CNN), a class of neural networks that employs convolutional layers to filter important information from images. For object recognition, CNN filters out information about the shape of objects, while in other kinds of elements, like birds for instance, it focuses more on color differences, as different types of birds have more distinct color differences than shape differences.
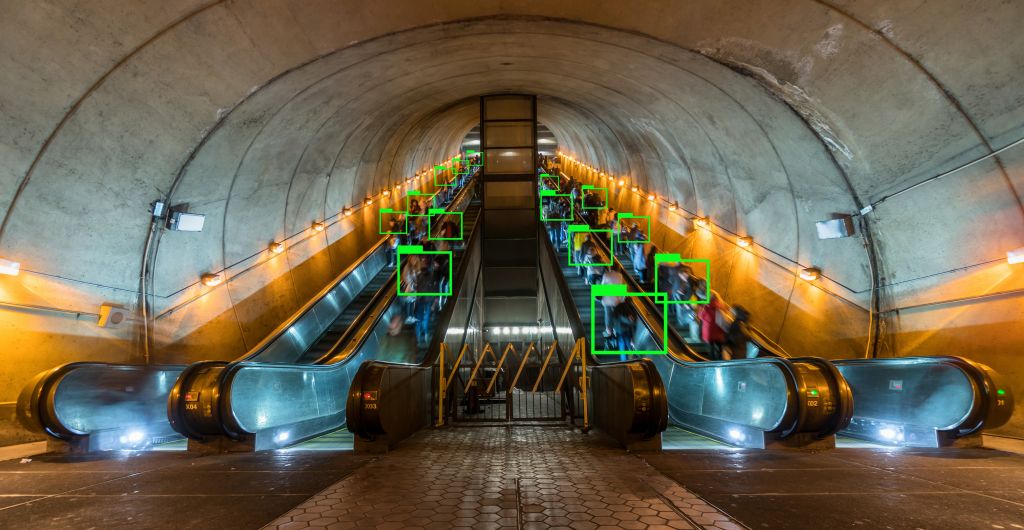

Machine Vision operates through high-definition cameras capturing environmental images. Beyond cameras, lighting, specific lenses, and sensors are prerequisites. This setup allows the system to surpass human vision capabilities, achieving magnetic levels of infrared, ultraviolet, and X-ray.
Machine Vision has been showcasing stronger effects in the industry, particularly excelling in process control, corrosion and anomaly identification, quality inspection, and safety systems. However, its benefits are slowly reaching all areas of society, showing a future that holds boundless possibilities, and nurturing entrepreneurship and innovation.
Deep Learning
Deep learning algorithms are the essence of Artificial Intelligence. They replicate the functioning of the human brain by processing structured and unstructured data. These algorithms can determine on their own which features are most important in distinguishing one object from another. Deep learning differentiates from other machine learning models in how each algorithm learns and how much data each type of algorithm uses. These models are highly adaptable and can be applied to a wide range of domains.
By integrating human expertise into the algorithm’s learning method, it produces a much more efficient, sustainable, and reliable result. In this context, the ideal application scenario consists of having a human training and monitoring the AI outputs, reporting its occasional errors so the technology can constantly correct its behavior for a more accurate analysis.

This tool is facilitating a range of activities, changing how humans face their reality, but it still needs improvement to be disseminated. Striking the balance between the autonomy of deep learning algorithms and the wisdom of human oversight will be integral to shaping a future where AI potentializes our capabilities while remaining aligned with human values and objectives.
Generative AI
Generative AI refers to a subgenre of artificial intelligence algorithms that are designed to create new, original information rather than just analyzing or processing existing data. As examples of Generative AIs, there are platforms such as ChatGPT and DALL-e that were responsible for AI’s recent boom. These models have the ability to produce diverse forms of content, such as images, text, music, and even videos, that exhibit impressive accuracy compared to human work.
The models are powered by neural networks and trained on extensive datasets. They learn patterns, context, and semantic relationships from data. During training, parameters are fine-tuned to minimize prediction errors. When generating new media, the AI starts with a prompt and generates semantic outputs, such as words, frames of a video or audio frequencies based on learned patterns.
It could be said that Generative AIs are the most widespread in today’s society. According to a recent McKinsey survey, 79% of all respondents say they’ve had at least some exposure to gen AI, either for work or outside of work, and 22% say they are regularly using it in their own work. Beyond that, GenAI is a key tool for companies managing data lakes.
Data lakes: a centralized repository that allows you to store and manage vast amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data at any scale.
Data lakes resemble to untidy sheds full of rubble. They consist as a useful storage for companies looking to put information in one place. However, the vast amount of data that companies generate requires an optimized strategy for contextualizing data, and a Generative AI plays a pivotal role in this task. This tool, when strategically applied, allows a proper data analysis, enhancing the efficiency, quality, and utility of data by automating tasks and supporting decision-making processes
Why AI alone won’t do the job
In the knowledge of AI’s strengths, it’s important to understand why this technology has its concerns and limitations around the industry. As AI systems continue to advance in complexity and capability, the need for human oversight remains a critical component of their deployment. While AI brings unmatched efficiency and analytical capabilities, it still lacks the comprehensive understanding, empathy, and ethical judgment that human operators possess.
For this reason, AI alone won’t do the job. In the energy industry context, there are intricate processes, regulations, and nuances that AI systems might not fully comprehend without human expertise. Besides that, human work is still inherently necessary for data collection and monitoring. The integration of human perspective and expertise is fundamental to reaching the AI’s full potential.
In addition, AI’s functioning is based on data provided to them, requiring large amounts of qualified information to properly operate. This means that the data given to the system can’t have any gaps or biases. By providing data that is accurate, representative, and unbiased, humans can ensure that AI systems are fair and effective. Otherwise, its ability to make decisions is based on incomplete or limited information.
In essence, AI’s capabilities fall short without human intervention. While AI can process and analyze vast amounts of data, it is the human perspective that provides context, interpretation, and domain-specific insights to the AI’s activities. By understanding how human work can be potentialized, these systems can be used in more effective ways. For this reason, Vidya’s platform is a perfect example of how integrating AI technologies, human expertise, and the company’s specific context generates much faster, more accurate, sustainable, and reliable results.
AI shaping tomorrow’s reality
As technology advances, AI is being applied to an increasing number of fields, offering innovative solutions and pushing the boundaries of what was once thought possible. Here are some key issues that AI is helping to solve:
Medicine: cancer diagnosis
AI is reshaping cancer diagnosis by meticulously analyzing subtle patterns and genetic alterations indicative of cancer in medical images, genetic data, and cellular structures . It aids pathologists in bridging the gap between genetic insights and clinical applications, enabling personalized treatments.
Agriculture: weather variation forecasting
AI models can analyze climate data and predict how changes in weather patterns might affect crop growth. This information helps farmers adapt their practices to mitigate the impact of weather oscillations.
Energy industry
The energy sector is undoubtedly one of the driving forces of today’s society. Beyond its importance in providing power to our daily activities, it is a highly valued sector that pioneers R&D later spread to the rest of society. However, those innovations do not come out of the blue, they emerge as solutions to problems that the industry needs to address.
Central to this industry is the Oil and Gas sector, an indispensable force that has shaped the course of global progress. This sector is not only responsible for driving industrial revolutions, but it became the backbone of transportation, enabling the mass production of automobiles, airplanes, and ships. In 2022, the O&G annual revenue was estimated at $4 trillion from an average of $1.5 trillion in recent years.
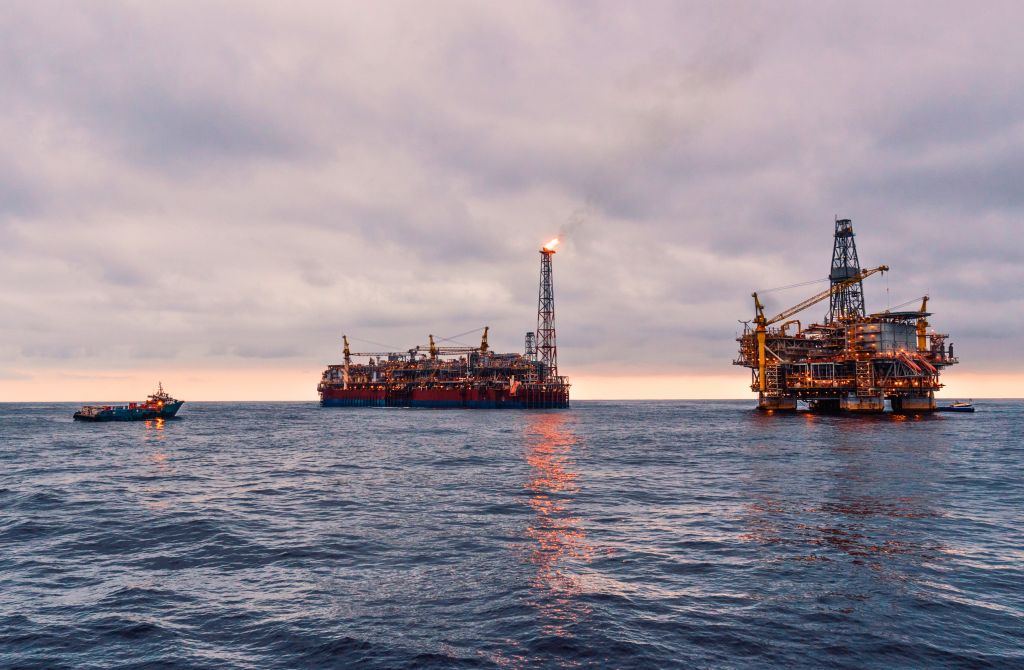

In this critical juncture, the oil and gas sector stands challenged to evolve. As the world grew more conscious of environmental impacts, the sector began seeking solutions, investing in cleaner technologies, and exploring sustainable practices. For this reason, let’s dive into some of the problems that AI is helping to solve in this industry.
POB management
People on Board represent an inherent challenge to the Oil and Gas industry, especially in the Upstream sector. It refers to the number of individuals present on a particular offshore platform, drilling rig, vessel or FPSO. The term is used to track and manage the workforce and ensure safety, resource allocation, and overall operational efficiency. In this sense, managing these numbers is a consequence of the inherent risks of Oil and Gas operations.
Operating in a naturally hazardous environment with a significant amount of flammable hydrocarbons requires careful management of People on Board (POB). Beyond that, unplanned events happen, which demands workers to solve the occurrence. This event harms the planning of the POB previously done and increases the downtime of the asset, which leads to significant financial losses and possible legal outcomes.
People on Board represent a valuable resource for asset management. It involves displacing professionals to the FPSO, which is not cheap, and exposing them to numerous risks. However, while reducing the POB count may appear straightforward, it is essential to have professionals to ensure the constant monitoring of the asset’s health. Therefore, it’s urgent that the industry rethinks how to make the most out of their POB avoiding resource waste and accidents.
In this sense, AI fits perfectly to digitally monitor the asset’s performance. AI-driven POB management delivers a much faster and more accurate operational panorama, doing the job faster in the combination of experienced workers + AI. In this new scenario, it will no longer take months to complete the process with hundreds of professionals, marking a much more efficient process that requires far fewer POB.
It is known that POB management encompasses a variety of obstacles, such as legal limitations on professionals onboard numbers and the impact of unplanned events leading to downtime and other financial losses. In this sense, remote inspections are playing a pivotal role in conducting the industry’s change of pace. By harnessing AI and moving towards digitalization, the oil and gas industry can improve safety, efficiency, and sustainability, while overcoming those challenges.
Corrosion detection
According to NACE, the global costs of corrosion are estimated to be US$2.5 trillion, which is equivalent to 3.4% of the global GDP (2013). Before AI, corrosion detection alone took months to be performed, allocating dozens of professionals to look around for anomalies in the whole facility. In addition, the inspection results are all handmade, generating inaccurate decision making that must be based on paper reports.
While the in-person visual inspection allocates professionals to execute several aspects of the process, such as difficult-to-access areas, following manuals with hundreds of pages for visual identification and setting up a spreadsheet that reports each corrosion point; AI-powered corrosion detection generates a traceable and auditable diagnosis. It acts as a catalyst for identification by using pattern recognition (Machine Vision) and deep learning algorithms. This way, computers can teach themselves about the context of visual data by “looking” at all data and teaching themself to tell one image from another.
AI-powered corrosion detection uses drones and sensors to digitally map the asset, which allows a real-time monitoring of the asset’s health. This indicates a much more complete detection than usual, reducing the downtime of the asset and the number of POB required. As a result, the HSE aspects (Health, Safety and Environment) are significantly improved, showcasing the company’s commitment to the industry’s growth and sustainability.
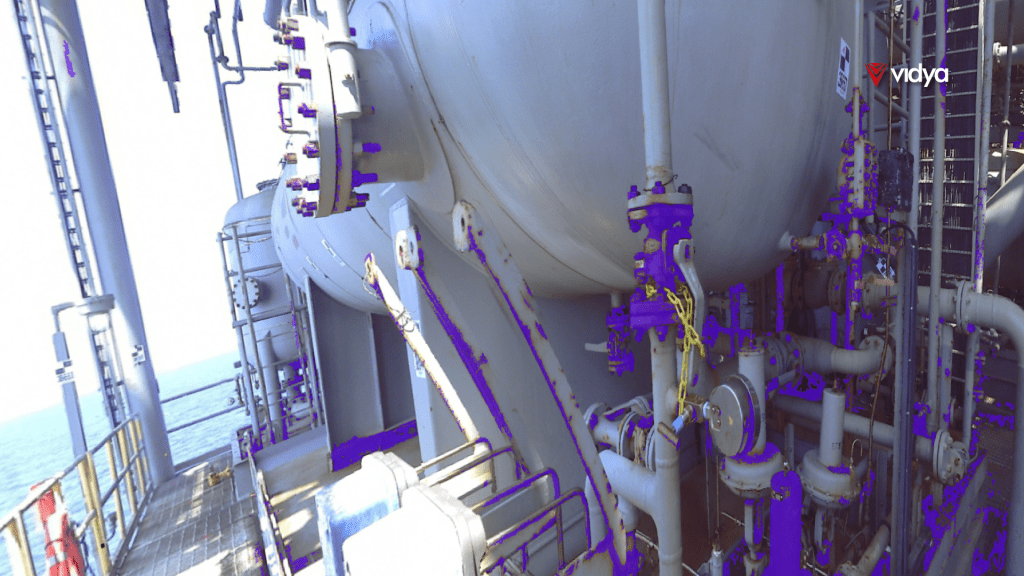
By adopting an optimized AI-powered platform for corrosion control, more anomalies are found in far less time than the usual approach. We deliver a significant upgrade in addressing inherent risks, time constraints, and inefficiencies associated with traditional methods. While corrosion treatment based on visual observations and paper reports are getting obsolete, our approach emerges as a critical tool to safeguard assets, increase efficiency, and truly commit to sustainable growth.
Predictive Maintenance
The use of AI-powered predictive maintenance can avoid costly unplanned downtime. By continuously monitoring equipment data, predictive maintenance pinpoints patterns and identifies potential issues, allowing your maintenance team to address problems early. Beyond that, this technology is allowing industries to rethink their approach to data-driven results.
While other maintenance methods implicate in paralyzing the asset activities, AI-driven predictive maintenance reports when it’s the best moment to execute support services. For instance, not-optimized preventive maintenance can’t predict machinery failures. Thus, it generates the need for an optimized maintenance plan.
The process consists in using historical data and analytics to forecast when an asset will fail and to identify the root cause of the problem. By adopting pattern recognition algorithms such as Computer Vision, the system can better detect hidden defects and damaged areas that could be difficult to locate in a visual manner. Other tools like analytic models predict when an anomaly occurs, facilitating the maintenance scheduling by predicting the degradation state of the asset in the long term.
This is how Vidya drives predictive maintenance, optimizing structure treatment and maintenance schedule. This advanced analytics approach takes into account thousands of variables and constraints to help operators figure out what decision to make in order to maximize profits. Our result is a tool that identifies small problems before they turn into big failures.
Vidya’s AI
Vidya’s platform integrates a variety of AI models to provide the most accurate and efficient result possible. Our approach acknowledges your prime concerns and the initiatives that are being taken to try to solve them. Furthermore, optimize industrial asset efficiency, reliability, and cut costs through our cutting-edge AI technologies. Here are our resources to enhance your operation: