Intro
In today’s rapidly evolving world, digital solutions are reshaping industrial standards for efficiency, safety and innovation. They’ve become a game-changer for facilitating multiple industrial and business related tasks such as process automation, anomaly detection, scenario visualization and decision making. This transformation is not merely a trend but a fundamental change that is rebuilding the landscape of industries worldwide.
“Digital transformation is not about technology; it’s about solving problems. It’s about using technology to make our lives better.” – Eric Schmidt, former CEO of Google
And, on the edge of Industry 4.0, Digital Solutions are pushing boundaries in enhancing industrial efficiency, safety and innovation. However, this concept cannot be streamlined to a single solution, being necessary to explore how the main frontiers of this new era are establishing change in industrial operations.
In this paradigm shift, let’s explore the main digital solutions that are changing how industries face their routines.
1. Computer Vision
Computer Vision allows computers to develop visual perception in the same way humans do. It functions through high-definition cameras that capture images from the surrounding environment. This technology is allowing companies to detect and address minimum anomalies that were previously hard-to-reach with a non-optimized strategy.
In this sense, Computer Vision processes images as information through visual refinement algorithms, where filters are used to enable the recognition of behavioral patterns in the images. In this context, filters are programmed to extract the most relevant information for a specific task. This means that the system can precisely extract information about the object’s shape, color and area, facilitating identification for anomalies such as corrosion.
Beyond that, using Computer Vision algorithms enables constant monitoring of the object’s conditions, allowing operators to accurately determine the anomaly’s scalability and overall impact. This technology is reducing costs and unplanned downtime while allowing workers to do non-mechanized tasks.
If you want to learn more about Machine Vision, click here.
2. Digital Twin
Digital Twin consists of a digital replica of an environment based on a constant stream of data flowing from the real world to the digital world and vice versa. This technology has the capacity to digitalize large-scale physical environments with high accuracy from real images collected in the field. Later, the images are linked into 3D digital models, being essential for monitoring asset integrity and performance. It can be used to simulate and test different scenarios before they are implemented in the real world.
In this context, companies can achieve clearer problem visualization and optimize maintenance planning while navigating through every corner of the digital asset. Digital Twin mirrors any piece of equipment, machines or even entire assets in order to get the most customizable and optimized outcomes. However, for mirroring to take place, a continuous flow of data must be established on both sides (digital and real). This way, operators can perform constant monitoring of the physical object while manipulating the digital model.
According to a Business Wire report, the digital twin market is expected to reach $4.8 billion by 2027. Which is not surprising if this technology’s abrasive capacities are considered, being able to enhance industrial structure, processes, and operations. In essence, Digital Twin models are allowing industries to have greater control over their operations, being able to visualize improvement points and simulate scenarios.
3. Robot Use
As technology advances and customer demand rises, the use of robots in industrial facilities continues to grow. In this ever-changing scenario, automations that were considered impossible are now part of routine activities. Indeed, adopting advanced robotics for industrial operations fostered creativity and more informed decisions by streamlining the execution of repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
In this sense, using robots is helping large industries to keep pace with increasing consumer demand. These tools are highly adaptable to different contexts, performing automated inspections, coating activities, and speeding up production, among numerous possibilities. In the Oil and Gas industry, for example, the use of Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) for offshore operations enable asset inspections within the subsea, which would be risky, challenging and time-consuming if performed with a human diver.
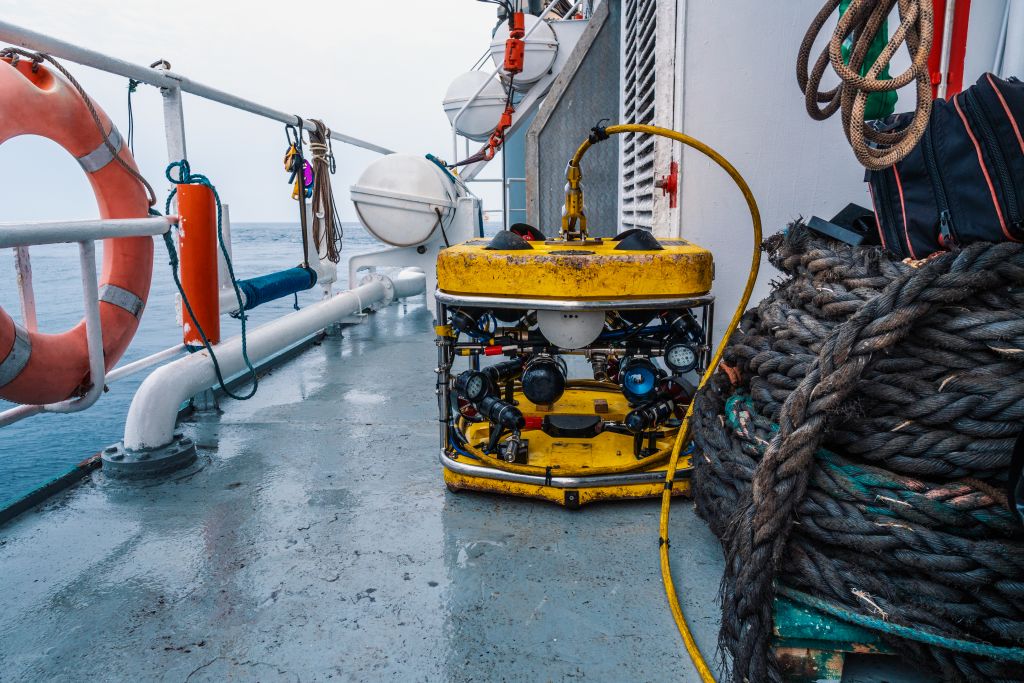

Beyond that, while the initial investment in robots can be high, the long-term savings in labor costs, increased productivity, and reduced waste can lead to significant cost reductions. According to Zippia, implementing robots saves companies up to about 20% in costs, and it is expected to hit 22% by 2025. For this reason, this abrasive frontier of digital solutions represents a significant change of pace in how industries address their bottlenecks.
4. Prediction models
Prediction models consist of algorithms that can foresee the behavior of certain assets in advance, allowing industries to make more informed decisions. By analyzing historical patterns, market trends, and various external factors, AI-driven forecasting models can provide insights that traditional methods might overlook. In this sense, industries can schedule maintenance in optimal time, simulate scenarios with different resource allocation possibilities and address minimal errors before they turn into big mistakes.
The ability of AI to detect subtle correlations and predict potential outcomes based on complex interactions enables organizations to anticipate changes and adjust their strategies accordingly. Unlike human planners, this advanced analytics approach takes into account thousands of variables and constraints to help operators figure out what decision to make in order to maximize profits.
For instance, in the Oil and Gas industry, AI-powered predictive maintenance can avoid costly unplanned downtime. This system generates a traceable and auditable diagnosis that allows operators to make more data-driven decisions. Beyond that, prediction algorithms can determine equipment degradation state over time by associating patterns with outcomes and then detecting learned patterns in new data. This constant monitoring enables safety improvements and reduction of environmental impacts.
If you want to learn more about AI-driven predictive maintenance, click here.
Conclusion
The digital frontiers previously discussed are not just trends; they are fundamental drivers of efficiency, safety, and innovation in various industries. In this sense, this abrasive concept is changing how operations face their routines, providing greater control over process compliance. This allows not only cost savings but also improvements in health, safety and environmental standards (HSE).
As we stand on the edge of Industry 4.0, it is clear that embracing these solutions is essential for staying competitive in an ever-evolving global landscape. Besides that, they represent frontline innovations of today’s technological revolution.In essence, Digital Solutions indeed make lives better, transforming industries, and paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable future.



