Steel industries, one of the oldest and most significant sectors in the global market, has faced long-standing challenges that stem from the inherent rigidity of its processes and the often harsh operating environments it encounters.
Despite these complexities, the imperative for innovation within this sector remains essential.
In this post, we delve into the primary challenges that the steel industry confronts, with the aim of shedding light on the critical areas that require innovation and process optimization.
The historical significance and widespread influence of the steel industry cannot be overstated. Its products form the backbone of countless sectors, ranging from construction and infrastructure to automotive and manufacturing. However, the industry grapples with multifaceted challenges that hinder its ability to adapt swiftly to changing market dynamics and emerging technologies.
4 Major Challenges to the Steel Industry
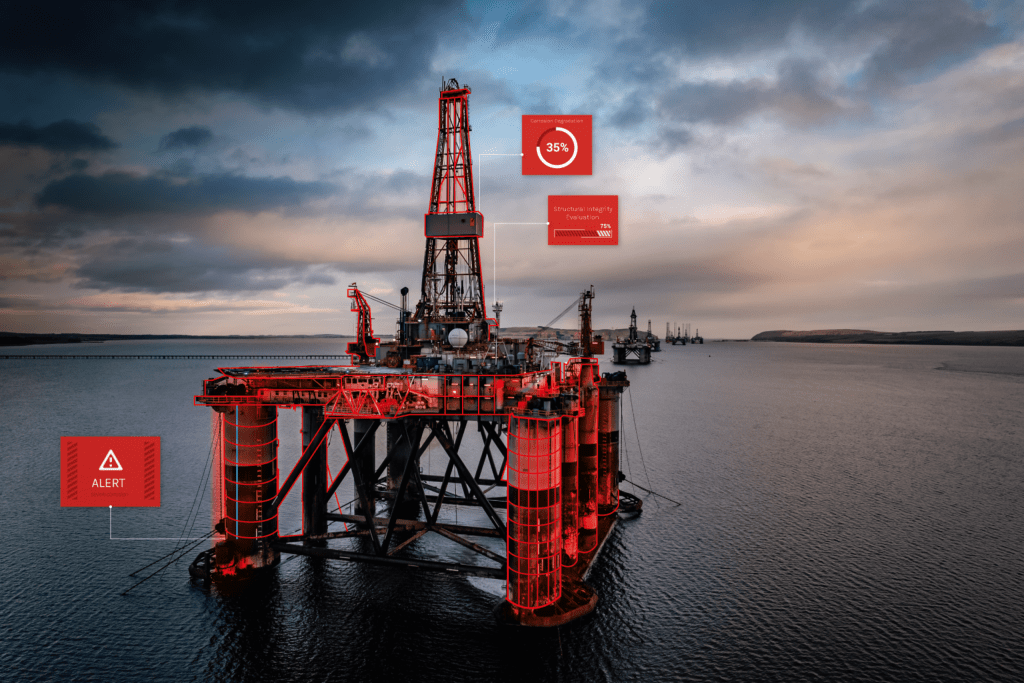
1. Harsh environment and asset failure
The steel industry heavily relies on high-temperature thermal or chemical transformations to achieve the desired final outcome. However, this kind of operational environment inherently poses significant risks, making it exceptionally challenging to prevent unexpected accidents and ensure worker safety.
Compounding these concerns, the inspection and maintenance of machinery and structures within the industry present ongoing difficulties. These vital components are susceptible to corrosion, wear, and tear, and structural integrity issues, often situated in hard-to-reach locations. Furthermore, as we will delve into later, workers frequently navigate through analog processes, lacking clear insight into the real priorities of the operation.
Consequently, beyond the physical degradation of the plant infrastructure itself, the work environment becomes inherently unsafe and stressful for employees. In certain cases, due to the extreme temperatures associated with steel production, operators are subject to strict time limitations, restricting their actions and overall efficiency. These restrictions further exacerbate the challenges faced by workers, limiting their ability to perform critical tasks and compromising their well-being.
Given these circumstances, it is imperative to prioritize the development and implementation of innovative solutions that address the safety and efficiency concerns within these operations. By embracing emerging technologies and process optimization, it becomes possible to create a safer and more conducive work environment for operators.
For instance, leveraging advanced inspection techniques, such as non-destructive testing and remote monitoring, can facilitate the timely detection of structural issues and corrosion, enabling proactive maintenance. Additionally, the adoption of digital solutions, including automation, robotics, and data analytics, can enhance worker safety by minimizing their exposure to hazardous conditions and improving overall operational efficiency.
By investing in modernization and digital transformation, the steel industry can empower its workforce with tools and technologies that alleviate safety concerns and reduce the stress associated with demanding operational conditions. Ultimately, prioritizing worker well-being and safety fosters a positive work environment, enhances productivity, and contributes to the long-term sustainability and competitiveness of the industry.
Understand How Vidya is empowering better Steel Operations by Filling out the form below
2. Process monitoring
The inspection and monitoring process within steel mills typically adheres to specific procedures, necessitating workers to operate using conventional analog methods.
Given the critical nature of the environment, halting production for corrective actions is often impractical. Unfortunately, the current monitoring approach falls short of predicting failures with the same level of accuracy as intelligent predictive models. This significant disparity highlights an inherent gap that leaves room for potential errors and inefficiencies.
To address these challenges, it is crucial to transition towards a more advanced and proactive approach to inspection and monitoring within steel mills. By embracing intelligent predictive models, the industry can significantly enhance its ability to identify and anticipate potential failures before they occur.
Adopting such intelligent predictive models allows for an accurate and efficient approach to maintenance, reducing the reliance on reactive measures and minimizing unplanned downtime. By identifying potential issues in advance, operators can schedule maintenance activities during planned downtime or during periods of lower production demand, optimizing the use of resources.
3. Maintenance
In addition to the inherent challenges mentioned earlier, conducting inspections itself becomes a daunting task. However, the complexity doesn’t end there—maintenance of encountered issues proves equally arduous.
Corrosion, a pervasive problem in these industries, significantly complicates the maintenance of equipment and structures due to the unforgiving operating conditions previously mentioned. Moreover, the multitude of intricate processes within the industry further exacerbates the issue by making it difficult to comprehend and utilize the extracted operational data effectively. The improper management of this information across disparate systems further hampers efficient maintenance of critical structures.
Consequently, the absence of precise management tools severely limits the ability to predict failures within operations, resulting in unplanned shutdowns and an overreliance on corrective maintenance methods. This approach not only disrupts production but also incurs unnecessary costs and prevents optimal resource allocation.
To address these challenges, it is crucial to adopt comprehensive solutions that enable effective inspection, streamlined maintenance, and robust data management within the steel industry.
4. Solid waste management and pollutant emissions
Another significant consequence stemming from the multitude of transformation processes within the steel industry is the generation of substantial volumes of subproducts that currently find no reuse within the operation. Consequently, a significant amount of waste is generated, and regrettably, a portion of this waste is improperly released into the environment.
Moreover, the primary source of energy for these industrial processes predominantly relies on the combustion of fossil fuels. This reliance directly contributes to the emission of polluting gases into the atmosphere. Both the improper waste disposal and the high carbon emissions associated with fossil fuel combustion pose severe environmental problems, effectively categorizing the steel industry as one of the most environmentally polluting sectors.
To address these environmental challenges and promote sustainable practices within the industry, embracing digital transformation is paramount.
Conclusion
The rigidity of the steel industry’s processes makes it suffer from several problems as a result. From the challenges in inspection and maintenance of the operation to the large emission of pollutants into the environment, this sector needs to find ways to optimize its processes to keep on satisfying the consumers’ and production demands, but in a more efficient and sustainable way.
The reuse of residual materials, the energy transition, and the adoption of technologies in the operation have been the three main paths adopted by this segment to overcome the covered problems. Click here to learn more!