As industrial processes become increasingly complex, more data are collected by sensors and technologies from digital transformation. However, this gathered information is not always centralized and contextualized, making the process of asset integrity management even more difficult.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution and the increased investment in new technologies by companies are constantly generating better results in their processes. One of the main gains from this is the improvement of the Operation and Maintenance phase of the industry (one of the most enduring stages of Project Lifecycle Management) with tools that keep up with the complexity of the operation and digitalize the industrial environment, making it increasingly data-driven.
But are the implementation and development of new technologies really the main lever to optimize the industry’s needs? To answer this question, it is important to understand more about the challenges present in the Industrial Operation and Maintenance stage of PLM and what are the benefits of digital transformation in this scenario.
First of all, what is PLM?
Project Lifecycle Management is a project management methodology grouped into stages that can be split and described in different ways, but the needs of any project will remain the same. A common and very detailed division uses 6 stages to explain the concepts of PLM:
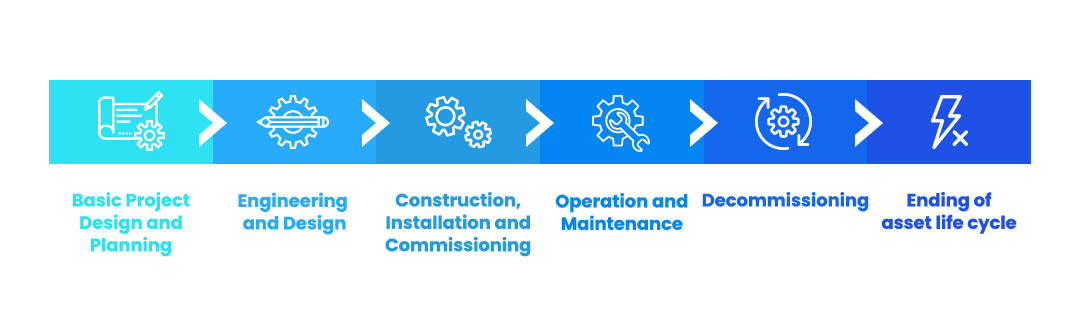
- Basic Project Design and Planning;
- Engineering and Design;
- Construction, Installation and Commissioning;
- Operation and Maintenance;
- Decommissioning;
- Ending of asset life cycle.
Stages 1 to 3 are the planning and development of the project structure itself. In other words, these three initial steps go from the evaluation of the project’s objective, and the budgeting of materials, to the construction and finalization of the asset’s structure.
In the fourth stage, Operation and Maintenance (O&M), the asset, structure or machine starts its operation, generating results and performing pre-defined objectives and actions, and is maintained so that its efficiency is the highest possible, increasing its useful life and reducing risks. Finally, the last two stages represent the finalization of the process.
To understand more about the development of technologies to boost the industry’s results, such as better integration between systems, longer asset life, and more assertive monitoring of the operation, we will focus on the O&M phase that is the most impacted and benefited in this process.
O&M characteristics and its connection with digital transformation
As said before, this phase is characterized by the actual functioning of the industrial process. It is usually the longest one, and the implementation of new technologies seeks to further extend the lifetime and efficiency of the assets involved.
Some of the essential tasks during this stage are:
- Monitor the operation of all assets present in the industrial plant;
- Balance the cost of operation with the expected results;
- Perform constant maintenance to preserve the efficiency of the process;
- Ensure the safety of the workers.
Understand how Digital Twin technology can be applied to the Operate and Maintain phase
From these activities, however, several challenges arise, and it is important to understand how the implementation of technologies in the industrial environment can solve them.

Challenges
Analyzing the performance of a single asset can be challenging enough. Then, when monitoring an entire industrial plant, in which the number of assets can easily exceed 500,000, with thousands of pieces of equipment, parts, and structures, it is possible to get a sense of the magnitude of the challenge behind this process.
Because of this, and other common problems in industry, it is possible to identify the main challenges faced in industrial operation and maintenance:
- The use of low automated and technological maintenance methodologies makes the industrial environment very susceptible to generating unexpected problems and increasing operation costs;
- Poorly centralized data about the industrial process and use of diffuse task management systems, generating great loss of information over time;
- Difficulty in analyzing the large amount of information generated all the time, and sometimes little digitalization of this data processing and analysis;
- Difficulty in identifying problems and making quick and agile strategic decisions, generating unplanned downtime in the operation;
- Limited budget to deal with the challenges presented in the industrial plant;
- Workers very susceptible to accidents in the workplace.
How digital transformation can boost operation and maintenance
Finally, now understand the context of the O&M phase and the common challenges presented by the industry at this stage, it becomes easier to relate the importance of digitalization within the scenarios described.
First, one of the biggest benefits offered by digital transformation in the industry was the ability to improve asset control through better collection and understanding of operational data. For example, sensors placed throughout the industrial plant can capture efficiency data from various equipment and make them available for operators anywhere in the world to evaluate, not needing them in the industrial plant in person.
In addition, with these technologies available in the market today (Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Digital Twin, among others), the industrial maintenance process has also developed a lot. Evolving from corrective maintenance, to preventive and even to the most technological and current ones, such as predictive and prescriptive, digital transformation increasingly allowed the improvement of the operation’s efficiency. Thus, the O&M phase has stopped just dealing with the problems that appear but has started to anticipate and prevent them from happening, avoiding unnecessary costs.
Conclusion
Although many industries still have challenges related to digital transformation, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is actually providing them with improved efficiency from the evolution of asset monitoring and maintenance.
The implementation of new technologies within the operation allows reduced time spent on activities, fewer operators in the field, fewer errors and unscheduled downtime, and consequently decreased production costs.
So, if the question was to understand if the development of new technologies really is the main lever to optimize the needs of the industry, the answer is for sure. Now it is only necessary to understand when to start applying these technologies in the operation!
If you want to know about one of the main technologies applied to the Operation and Maintenance phase and how it can improve data contextualization and decision-making, click here to discover the Digital Twin and its applications!